If you often experience bloating during the winter months, you’re not alone. Bloating is a common digestive issue, and the colder weather can exacerbate the symptoms. However, by making a few adjustments to your diet and lifestyle, you can prevent bloating and promote better digestive health.
In this article, we will provide practical tips on how to prevent bloating during winter. We’ll also explore what constitutes a balanced diet and how it can contribute to digestive health. By following these tips and adopting a balanced diet, you can alleviate bloating and maintain better health throughout the season.
Table of Contents

Key Takeaways
- Consuming excessive gas-producing foods, decreased physical activity, and decreased water intake can contribute to bloating during winter
- Practical tips for preventing bloating during winter include dietary adjustments and lifestyle changes
- Incorporating seasonal foods in your diet and having a balanced diet can help prevent bloating
- A balanced diet entails essential components such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
- Optimal distribution of macronutrients and staying hydrated can help prevent bloating
The Causes of Bloating in Winter

The chill of winter makes us crave comfort foods to stay cozy. However, consuming excessive gas-producing foods, such as beans, lentils, and cruciferous vegetables, can lead to bloating. Moreover, decreased physical activity due to the cold weather and being indoors for longer periods can also slow down digestion, causing bloating. Decreased water intake is also common in winters, which can lead to dehydration-related bloating.
To sum up, the main causes of bloating in winter are:
- Consuming gas-producing foods
- Decreased physical activity
- Decreased water intake
“Winter bloating is a common issue due to consuming excess comfort foods while staying immobile and dehydrated. It’s essential to understand these causes to prevent and alleviate bloating”.
Bloating after Eating Food
Certainly! Bloating after eating food can occur due to various reasons. Here are some common causes and tips to help alleviate bloating:
- Overeating: Eating too much food in one sitting can overload your digestive system, causing bloating. Try to eat smaller, more frequent meals.
- Eating too fast: When you eat quickly, you might swallow air along with your food, leading to bloating. Slow down and chew your food thoroughly.
- Gas-producing foods: Some foods, such as beans, broccoli, cabbage, onions, and carbonated drinks, can cause gas and bloating in some individuals. Identify and limit these foods if they cause discomfort.
- Food intolerances: Intolerance to certain foods, such as lactose or gluten, can lead to bloating. Consider keeping a food diary to track what you eat and any symptoms that follow.
- Eating fatty foods: High-fat foods can delay stomach emptying, leading to bloating. Opt for lighter, healthier options.
- Carbonated drinks: Carbonated beverages can introduce air into the digestive system, causing bloating. Try to limit or avoid them.
- Eating habits: Eating late at night or lying down immediately after a meal can contribute to bloating. Aim to eat at least a few hours before bedtime and remain upright after eating.
- Food allergies: Allergies to certain foods can cause bloating. Consult with a healthcare professional for allergy testing if you suspect this might be the case.
- Medical conditions: Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), celiac disease, or other digestive disorders can cause bloating. If you have persistent or severe bloating, it’s essential to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help your digestive system function properly.
Bloating Symptoms
Bloating can manifest with various symptoms, which can include:
- Abdominal Discomfort: Feeling a full or tight abdomen, often accompanied by a sensation of pressure or distension in the stomach area.
- Visible Swelling: The abdomen might visibly swell or appear larger than usual due to the accumulation of gas or fluid.
- Gas and Flatulence: Experiencing increased gas production, leading to frequent burping or passing gas.
- Feeling of Fullness: Even after eating small amounts of food, a bloated person might feel excessively full.
- Cramping or Pain: Some individuals may experience abdominal cramps or mild to moderate pain associated with bloating.
- Changes in Bowel Movements: Bloating can sometimes coincide with changes in bowel habits, including constipation or diarrhea.
- Discomfort Moving or Sitting: The sensation of bloating might make movement or sitting in certain positions uncomfortable or difficult.
- Indigestion or Heartburn: Bloating can be accompanied by symptoms of indigestion, such as heartburn or a burning sensation in the chest.
It’s important to note that bloating can have various underlying causes, ranging from dietary choices to medical conditions. Occasional bloating might not be a cause for concern, especially if it’s associated with particular foods or temporary factors. However, persistent or severe bloating, especially when accompanied by other concerning symptoms like significant weight loss, blood in stool, or severe pain, should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out any serious underlying conditions.
Bloating and Brain Fog
Bloating and brain fog can sometimes be related, although they are separate symptoms. Bloating, often related to digestive issues, might indirectly affect cognitive function and contribute to brain fog in some cases. Here are a few potential connections and suggestions:
- Gut-Brain Connection: The gut and brain are interconnected through what’s known as the gut-brain axis. Digestive issues, such as bloating or discomfort, can sometimes trigger or exacerbate brain fog. The discomfort and distress caused by bloating might impact cognitive function.
- Inflammation: Bloating can sometimes be a sign of inflammation in the gut. Inflammatory responses in the body might affect the brain and contribute to feelings of fogginess or clouded thinking.
- Food Sensitivities or Intolerances: Bloating can be a symptom of food intolerances or sensitivities. Sometimes, consuming foods that your body can’t tolerate well might lead not only to digestive issues but also to brain fog and fatigue.
- Nutrient Absorption: Chronic bloating or digestive issues might interfere with nutrient absorption. Inadequate absorption of essential nutrients like vitamins and minerals can affect brain function and contribute to brain fog.
- Hydration: Dehydration can lead to both bloating and brain fog. Ensuring adequate hydration levels may help alleviate these symptoms.
Addressing both bloating and brain fog may involve:
- Dietary changes: Identify and limit foods that trigger bloating. Consider keeping a food diary to track any correlations between what you eat and your symptoms.
- Healthy eating habits: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Fiber-rich foods can aid digestion and reduce bloating.
- Staying hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration, which can worsen both bloating and brain fog.
- Managing stress: Stress can exacerbate digestive issues and cognitive problems. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga to help manage stress levels.
- Consulting a healthcare professional: If bloating and brain fog persist or worsen, it’s essential to consult with a doctor. They can help identify any underlying health conditions and provide appropriate guidance or treatment.
Understanding the possible links between bloating and brain fog can guide you in making lifestyle changes that may alleviate both symptoms. However, seeking professional medical advice is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Tips to Beat Bloating in Winter

Winter can bring about a myriad of digestive issues, bloating being one of the most prevalent. Fortunately, there are simple, yet effective ways to prevent bloating in winter:
- Avoid consuming gas-producing foods such as beans, broccoli, and carbonated drinks.
- Stay physically active to keep your digestive system moving. Even a short walk can help ease bloating and promote digestion.
- Incorporate probiotics into your diet, such as yogurt or kefir, to promote healthy gut bacteria.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, herbal teas, and warm broths.
- Be mindful while eating – avoid overeating, eat slowly, and chew your food well.
These tips will help to alleviate bloating and promote a comfortable digestive system throughout the winter season. So, make sure to tweak your diet and lifestyle for a healthier you this winter!
Incorporating Seasonal Foods in Your Diet
One effective way to prevent bloating during winter is to incorporate seasonal foods into your diet. Not only do seasonal foods offer a range of essential vitamins and minerals, but they also help maintain a healthy digestive system and reduce bloating.
The Nutritional Benefits of Winter Produce
Seasonal fruits and vegetables like pomegranates, citrus, cranberries, Brussels sprouts, kale, and squash are high in fiber and water content. These nutrients promote healthy digestion and prevent constipation, reducing bloating and discomfort in the gut. Additionally, seasonal produce tends to be fresher, more flavorful, and more accessible, contributing to a well-rounded and satisfying meal plan.
Including Variety in Your Diet
When incorporating seasonal foods into your diet, aim for a diverse mix of colors and flavors. This ensures that you’re consuming a wide range of nutrients and enjoying unique taste experiences. You can try roasting winter vegetables with herbs and spices, adding seasonal fruits to a salad, or making hearty soups with winter squash or root vegetables.
By including seasonal foods in your diet, you can achieve optimal digestive health and reduce bloating during winter. Not only are these foods packed with essential nutrients, but they also add variety and flavor to your meals.
Understanding the Elements of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential to a healthy lifestyle and well-being. It involves consuming the right amount of nutrients from a variety of foods to ensure that your body receives all the necessary nutrients for optimal health. A balanced diet comprises six essential components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Provides energy to fuel physical activity and organ function. |
| Proteins | Essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of the body’s tissues. |
| Fats | Provide energy and support the absorption of vitamins and minerals. |
| Vitamins | Essential for various bodily functions, including growth and development, immunity, and energy production. |
| Minerals | Essential for building strong bones and teeth, and supporting bodily functions such as the production of hormones and enzymes. |
| Water | Crucial for maintaining bodily functions, including digestion, hydration, and temperature regulation. |
Incorporating these essential components into our daily meals can help ensure that we obtain the nutrients needed to maintain good health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Here are some tips on how to incorporate them into your diet:
- Choose a variety of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and low-fat dairy products.
- Avoid foods that are high in added sugar, saturated and trans fats, and sodium.
- Eat moderate portions and keep track of calorie intake.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day, and limit sugary beverages and alcohol.
By adopting a balanced diet, you can improve your overall health, maintain a healthy weight, and prevent digestive issues such as bloating.
Balancing Macronutrients for Digestive Health
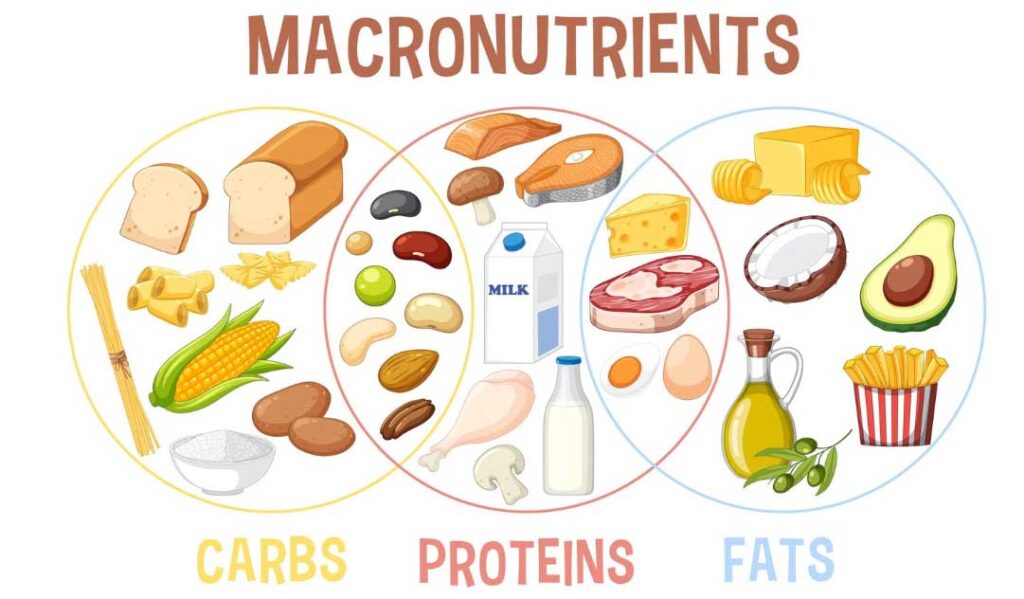
Macronutrients play a crucial role in promoting digestive health and preventing bloating. A balanced diet consists of an optimal distribution of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, each serving a unique purpose in maintaining a healthy digestive system.
| Macronutrient | Role | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Provide a primary source of energy for the body and play an essential role in digestion | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes |
| Proteins | Help build and repair tissues in the body, including the muscles used in digestion | Lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, nuts, seeds |
| Fats | Aid in nutrient absorption, protect organs, and serve as a source of energy | Avocado, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish |
A diet rich in macronutrients can help maintain a balanced digestive system, reducing the risk of bloating and discomfort. Remember to consume these nutrients in appropriate portions, balancing each to suit your dietary requirements and personal nutritional goals. Consult with a nutritionist or dietitian to help determine a balanced macronutrient distribution for your specific needs and goals.
Hydration and Digestion

Hydration plays a significant role in maintaining a healthy digestive system and preventing the discomfort of bloating. Adequate water intake helps in breaking down food and absorbing nutrients efficiently. Dehydration, on the other hand, can slow down the digestion process, leading to constipation and bloating.
It is recommended to drink eight glasses of water a day to maintain good health. However, the amount of water intake may vary depending on an individual’s body type, weight, and level of physical activity.
Hydration Tips for Optimal Digestion
- Drink a glass of water before meals to aid in digestion
- Incorporate foods with high water content such as cucumbers, watermelons, and tomatoes, to supplement your water intake
- Limit your alcohol and caffeine intake as they dehydrate the body
- Drink fluids at room temperature to enable the body to absorb them more effectively
By incorporating these hydration tips into your daily routine and drinking enough water, you can improve digestion and prevent bloating during the winter season.
Conclusion
By implementing the tips we’ve outlined in this article and understanding the principles of a balanced diet, you can say goodbye to winter bloating. Prioritizing healthy eating habits and staying hydrated are crucial elements that will contribute to a comfortable digestive system and better health throughout the winter season.
Remember, preventing bloating during winter requires intentional choices. It’s essential to introduce seasonal foods in your diet, consume foods that are high in fiber, and reduce your intake of gas-producing foods. Additionally, maintaining an active lifestyle, incorporating macronutrients, and staying hydrated will contribute to a balanced digestive system.
By following these tips, you’ll find that the winter season can be a time of healthy eating and overall well-being. Cheers to a comfortable and bloating-free winter!
FAQ
1. How can I prevent bloating during winter?
To prevent bloating during winter, you can follow these tips: avoid consuming excessive gas-producing foods, stay physically active, drink enough water, eat smaller, more frequent meals, and include fiber-rich foods in your diet.
2. What are the causes of bloating in winter?
Bloating during winter can be caused by factors such as consuming excessive gas-producing foods, decreased physical activity, decreased water intake, and changes in eating patterns.
3. How can I prevent bloating in winter?
To prevent bloating in winter, you can try these tips: avoid overeating, consume warm beverages, include ginger in your diet, stay hydrated, practice stress management techniques, and maintain a regular exercise routine.
4. Is it important to incorporate seasonal foods into my diet?
Yes, incorporating seasonal foods into your diet is beneficial as they are fresher, more nutritious, and can help prevent bloating. Winter produce such as root vegetables, winter greens, and citrus fruits are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
5. What constitutes a balanced diet?
A balanced diet consists of a variety of foods from all food groups, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is important to consume the right proportion of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) for overall well-being.
6. How can macronutrients contribute to digestive health?
Macronutrients play a crucial role in maintaining digestive health. Carbohydrates provide energy, fiber aids in digestion, proteins support tissue repair, and fats help in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Balancing these macronutrients is important for a healthy digestive system.
7. What is the connection between hydration and digestion?
Hydration is essential for optimal digestion. Drinking enough water helps soften stools, aids in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients, and supports the movement of food through the digestive tract. Staying properly hydrated can help prevent constipation and bloating.




